Financial reporting is one of the three audit objectives related to internal audit. The other two are compliance and operations. Here we will discuss part one out of three in the internal audit.
Here we primarily focused on the performance of actual internal audits for financial reporting.
This post is intended for a wide variety of people from students looking for supplemental study material to business owners interested in performing internal audits of their own companies. To job seekers looking to acquire knowledge to gain a competitive edge in the job market.

Definitions of key terms
Here we discuss some key internal audit definitions. Also, these are the most frequently used terms in the profession of internal audit.
Internal auditing:
An independent objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization’s operations.
Internal controls:
Any action was taken by management the board and other parties to manage risk and increase the likelihood that established objectives and goals will be achieved. Management plans organize and direct the performance of sufficient actions to provide reasonable assurance that objectives and goals will be achieved.
Governance:
The combination of processes and structures implemented by the board to inform direct manage and monitor the activities of the organization toward the achievement of its objectives.
Risks:
The possibility of an event occurring that will have an impact on the achievement of the objectives. Risk is measured in terms of impact and likelihood.
Business objectives:
The goals of an organization.
Compliance:
Providing assurance related to the design and operation of control activities and procedures in place to assure compliance with laws regulations policies etc.
Risk management:
A process to identify assess manage and control potential events or situations to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of the organization’s objectives.
Internal controls governance and risk management are linked activities and you must consider all three when examining any one of these elements.
Here is a question for you. Take some seconds and select your answer.
Which two terms are used to measure risk?
- Likelihood and control
- Impact in dollar amount
- Cost and control or
- Likelihood and impact
Do you find your Answer?
Your answer is 4.
Risk is measured in likelihood. The chance or probability of the risk event will occur and impact the effect on the organization. For example, the impact can cost to the company such as fines and penalties for inaccurate financial reporting to regulatory agencies.
Internal auditing
Internal auditing is an independent objective assurance and consulting activity. Designed to add value and improve an organization’s operations. It helps an organization accomplish its objectives by bringing a systematic disciplined approach to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk management control and governance processes.
Internal audits important
What is the benefit of an internal audit? The board of directors and senior management at organizations often rely on internal auditing for insight into whether the organization is functioning properly. And to see if strategic goals are being met.
Internal auditing can lead to business process improvements. More efficient operations and more reliable financial reporting. The code of ethics is incredibly important to the performance of internal audits. The results of a reliable audit are dependent upon the ethics of the auditor and four key ethical principles.
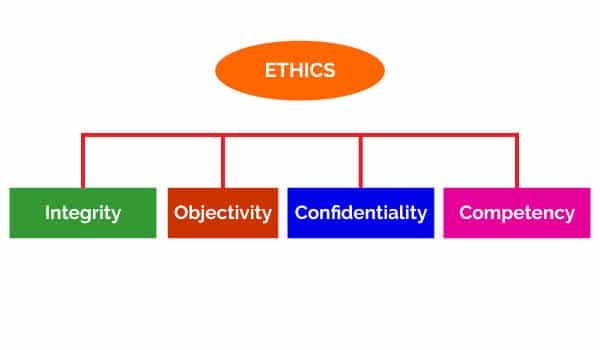
Integrity:
The integrity of internal auditors establishes trust and thus provides the basis for reliance on their judgment.
Objectivity:
Internal auditors exhibit the highest level of professional objectivity in gathering evaluating and communicating information about the activity or process being examined.
Confidentiality:
Internal auditors are expected to value the ownership of information they receive and not disclose information without the proper authority.
Competency:
Internal auditors apply the knowledge skills and experience needed in the performance of internal audit services.
Activities to manage the organization’s risks
Take place all across the organization from specific processes to entire business units to the entire organization. These are the key personnel who play the most critical role in risk management. The board audit committee and senior management set the tone at the top which is a positive internal environment for managing risks.
Controls over financial reporting
Controls over financial reporting or to ensure financial statements fairly present the financial condition of the organization. Financial reporting is the process of producing statements that disclose the organization’s financial status to management investors and the government. Financial reporting can also be used for operational activities as well.
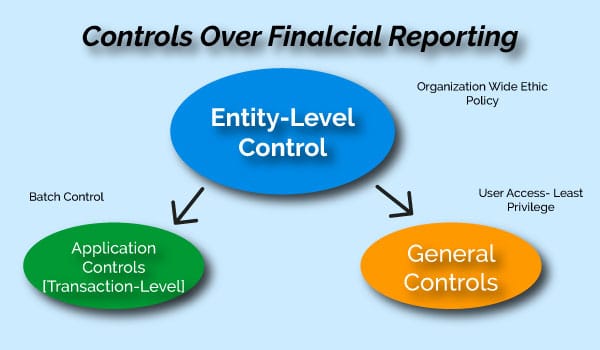
Entity level controls:
Entity level controls are the activities that help ensure management directives are carried out across the entire organization. An example of entity-level control is an organization-wide ethics policy.
General controls:
IT general controls apply to the entire system the infrastructure applications and data related to reliable financial information. An example of IT general control is the concept of least privilege and user access. The least privilege states that users should only have the level of access required to do their jobs.
Application controls:
Application controls were transaction-level controls relate to the activities ensuring objectives related to specific financial reporting objectives are achieved. An example is batch control. Batch controls keep track of the total dollar amount and number of transactions being processed in a group.
Financial statements
Our reports record the financial activities and position of a business person or other entity. The four primary types of reports are:
- The balance sheet
- The income statement
- The cash flow statement
- And the statement of owner’s equity
Other types of financial reports
There are many other types of financial reports such as consolidated income statements accounts receivable aging reports and vendor balance reports. In the post, we will discuss financial statements and some of the specific tests of controls balances, and transactions that can be performed.
The committee of sponsoring organizations or COSO is made up of five member organizations that include the AICPA and the in of internal auditors. Out of this organization came the coastal framework for internal controls.
Which consists of five interrelated components for describing and analyzing an organization’s internal control system. Keep these five components in mind during the performance of an internal control audit over financial reporting.
Audit framework & standards
Audit frameworks are important because these guidelines help to ensure consistent and appropriate audit practices. Other frameworks consist of a mission statement describing independence objectivity organizational ethics and professionalism.
Audit frameworks also include audit standards which are mandatory guidance and practice guides which are non-mandatory guidance used for various business activities.
Here is question No 02 for you. Take some seconds and select your answer.
What is the difference between an audit framework and audits standards?
- Standards are a part of an audit framework
- There is no difference
- Standards contain more information
- Frameworks contain more information
Do you find your answer?
The answer is 1.
Audit frameworks consist of mission statement standards which are mandatory guidance and non-mandatory guidance such as practice guides.
Question No 03:
Your manager would like to start an internal auditing department in the ABC company. She tasks you with the job. Where would you start?
- Immediately start planning your first audit.
- Establish or adopt an applicable internal audit framework that is approved by the board and audit committee.
- Draft your findings
- Discuss the risks that are applicable to the organization
Do you find your answer?
The answer is 2.
The first thing you should do is to establish an audit framework so that auditors will have guidelines to work within prior to performing any audience.
The audit engagement process
Here we will discuss the audit engagement process. When auditors perform an internal audit there are usually four steps. Planning, fieldwork, reporting, and follow-up. Also called the post-audit review the purpose of the planning phase is to reduce audit risk.
The risk the auditor fails to detect material misstatements and the financial statements which are reported to various regulatory entities. The fieldwork phase is designed to test controls transactions and balances and gather evidence.
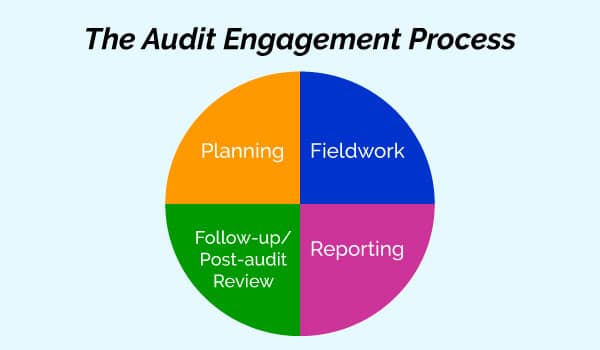
You will often conduct interviews of key staff members and communicate to management throughout the process regarding issues called findings. The reporting phase is where the audit report is drafted and findings are finalized.
The follow-up or post-audit phase is where auditors communicate with management about whether recommendations have been implemented or the timeline for implementing recommendations. The post-audit phase is also where auditors can modify and improve their own processes.
Question no #04 for you.
Which of the following occurs during the fieldwork phase of the audient?
- Drafting the recommendations
- Determining the audit scope
- Testing or
- Documenting findings
Do you find your answer?
The answer is 3.
The fieldwork phase is designed for examining or testing records and activities and gathering persuasive audit evidence the other answer choices occur in other phases of the audit engagement.
Evaluating evidence
When evaluating the quality of evidence used to support audit conclusions and recommendations, use the SRRU concept. Evidence must be sufficient, reliable, relevant, and useful. Sufficient evidence is convincing. Reliable evidence is strong and true. Relevant evidence is closely related to the audit subject. And useful evidence can be helpful in making audit conclusions.
Question no #05
Information that supports audit observations is…….?
- Useful.
- Relevant.
- Sufficient. Or
- Reliable.
The answer is 2. Relevant.
Relevant evidence is closely related to the audit subject. Therefore, relevant evidence supports audit observations by being related to the audit observations.
Audit objectives
The auditor’s objective is to express an opinion on the effectiveness of the company’s internal controls over financial reporting. Auditors identify risks, negative events, and controls activities. Internal auditors must obtain sufficient appropriate evidence to obtain reasonable assurance about whether material weaknesses exist.
Question no #06 for you. Take some time and select your answer.
In order to must obtain blank assurance as to whether a material weakness exists in regards to management’s assessment of internal controls over financial reporting.
- Absolute
- Enough
- Moderate or
- Reasonable
The answer is d reasonable.
Reasonable assurance is dependent on evidence that is sufficiently reliable relevant and useful.
Phases of the audit
In this section, we will discuss the four phases of the audit planning, fieldwork, reporting, and the follow-up or post-audit review.
Audit planning:
An audit of internal controls over financial reporting should be integrated with the audit of the financial statements and should include examinations of the following.
- Entity level controls our internal controls that ensure management directives are carried out.
- Management override refers to management’s ability to manipulate accounting records and prepare fraudulent statements even when controls appear to be working.
- Segregating duties is having more than one person perform a task to minimize the chance of error or fraud.
- Alternative controls are also called compensating controls and exist as a backup in case your primary control activities fail to prevent the risk event from occurring.
- General controls our it controls that apply to all system components.
- It application controls apply to transactions and data within a specific application.
- Staff should remain up-to-date in the appropriate ways to report financial statements.
Ongoing training is key. The nature and extent of audit documentation are related to obtaining sufficient and appropriate audit evidence.
Question no #07
Why are segregating duties important?
- Because it is a control activity designed to prevent fraud and error
- Because this is a risk event
- It is not important
- or Because duties should always be separated
The answer is 4
Segregation of duties is designed to ensure that more than one person completes a task. To minimize error and prevent fraud not all tasks need to be segregated but many do.
Audit planning for internal controls over financial reporting involves examining the organization’s industry. External and internal factors that may impact financial statements.
Determining preliminary materiality risk and other control weaknesses in order to develop procedures including the specific tests of controls balances and transactions and the types of evidence that will be gathered during audit fieldwork.
Question no #08
Why is it important to understand the entity in its environment?
- It is not important
- Because you can then identify controls
- Understanding the entity and its environment will help the auditor identify risks specific to the entity or
- Because all risks are external to the organization
The answer is 3
Understanding the company and its goals or objectives will help the auditor identify the risks that will prevent the company from meeting these objectives. For example, in the banking industry, it is important to protect client data. Protecting client data is objective. A risk to this objective is a cybersecurity threat. That exposes client data to identity theft.
Question no #09
How does performing a preliminary risk assessment improve audience?
- Risk-based audits are better aligned with organizational goals
- Risk identification does not help auditors
- It is required by law or
- Primary risk assessments can be modified later
The answer is 1
Identifying risks and designing activities or controls to prevent risks will help organizations reach their goals. This is the purpose of internal auditing.
An audit planning primary risk assessment help auditors scope their audits. Because knowing the risks will help auditors determine the records to examine. People to interview and test to perform. The auditor uses its best judgment to select the period of time to examine. And the auditor writes down in detail how the work will be performed. The audit work plan is usually approved by management prior to beginning fieldwork.
Question no #10
How do auditors determine the types of records they will examine?
- Auditors must guess the types of records they will examine
- Auditors are directed by operating managers as to which records to examine
- Do not examine records or
- Auditors first identify the risk events that may impact the organization
The answer is 4
Honors first identify the risk events that may impact the organization. Then identify the activities and records to document the prevention and detection of these risk events so that they can be examined.
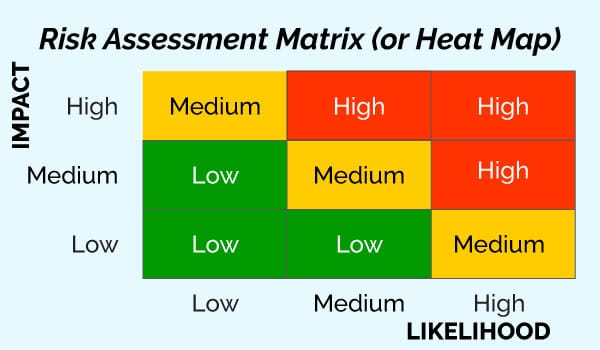
Here’s a simple risk assessment matrix in the planning phase the auditor will determine whether a risk is low medium or high and this will help to determine the extent or the amount of testing that will take place.
Memo of the discussion template
This is the memo of discussion. The first section is where you will describe the meeting purpose. The second section is where the auditor preparing the document lists their information. The third section is where the audit team is listed. To add more rows. Go to the Display tab and select add below. The fourth section is where you list either the audited business unit or your management if this is an audit planning meeting.


Download the template from here.
Internal control template
There is an internal control checklist. This template will help you go from a very general idea of controls or the activities that prevent or detect risk to specific procedures that you can use to develop your audit work plan for fieldwork testing.

This is the internal controls assessment template. In this tab, the internal controls assessment instructions will provide instructions and guidance on what to enter into each cell. These are detailed instructions for developing and documenting internal controls at your organization.

This is the internal controls assessment template tab. Here you will enter your actual data for your internal controls audit. If you forget what you should enter into any of the cells, go back to the instruction tab for guidance.

Download the template from here.
In the last tab, the example for sales transactions objectives, we see how the financial statement assertions are related to the financial statement objectives we will be auditing. For example, if the auditor is concerned about the completeness of sales transactions, he or she may wish to see if existing sales transactions are recorded.
To do this. The auditor may examine a sample of sales invoices to see if they were all recorded in the accounting system and reflected on the income statement in the sales account.
Audit work plan template
Here is the most important planning phase document. The audit work plan. At the top of the document, we provide the audit project details including the project name the business level that will be examined and the source of the audit. Here we will also list the number of auditors need to perform this audit and whether contractor assistance is necessary.
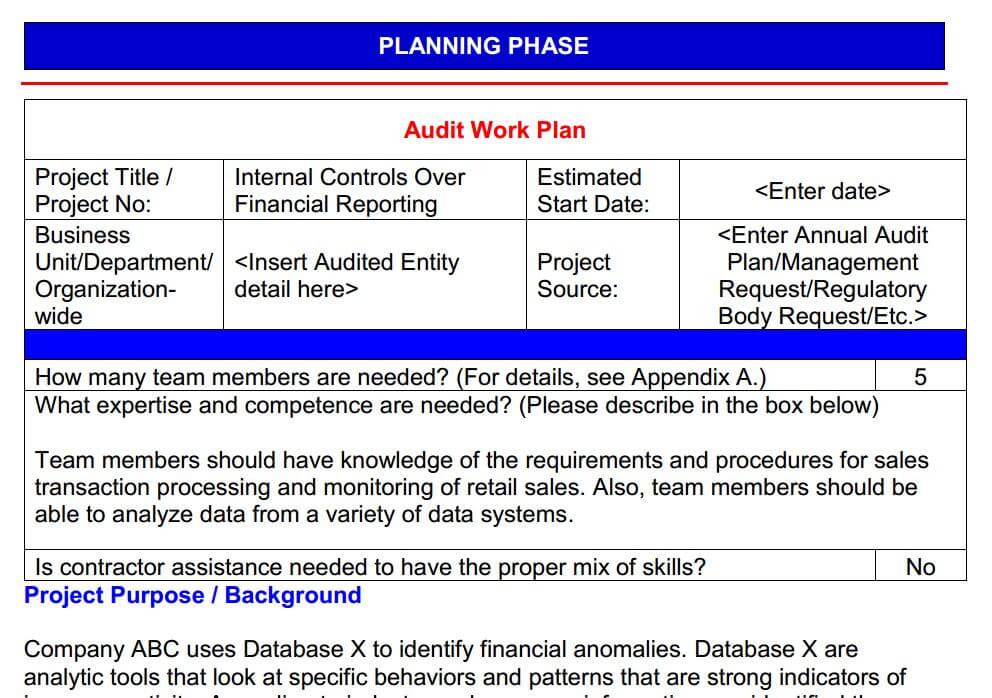
The project purpose and background section are designed to provide a high-level overview of the audit subject. Based on our initial risk assessments we will likely have areas to focus on when performing our internal controls audits over financial reporting. In this example, the assessments will concern cash sales inventory and depreciation. The scope here is listed here as well as our audit objective.
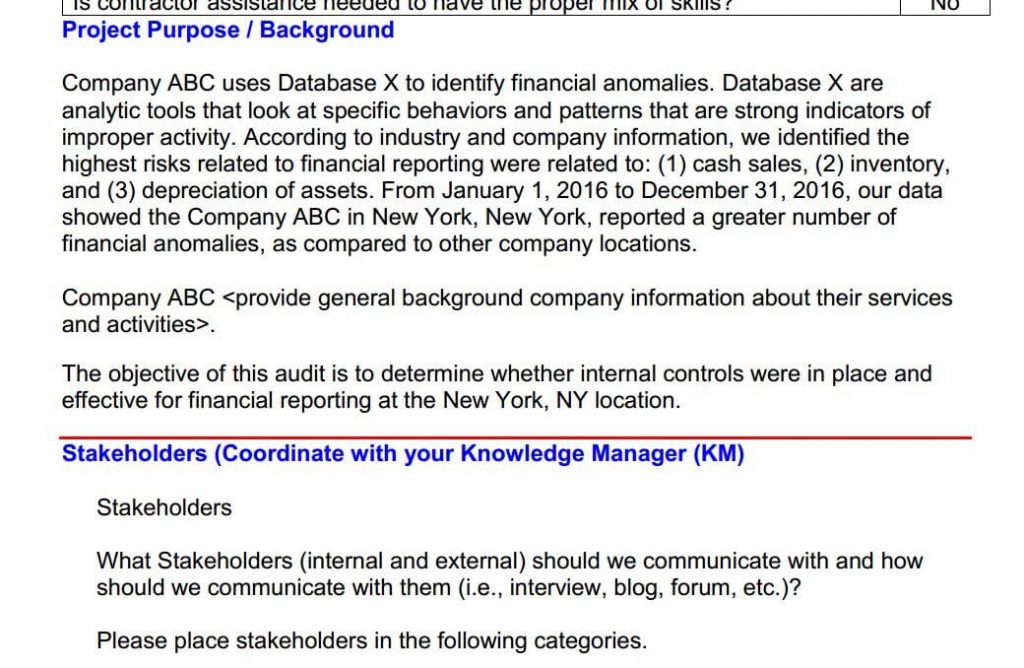
The stakeholder section is next. Identifying and communicating with stakeholders is very important to an audit. Stakeholders our internal and external parties with interests related to the audit subject. Here our stakeholders are in categories which include clients decision-makers, owners of the processes, we are examining, users of the systems being examined and consumers.

The product description section is where you will explain the type of audit deliverable produced at the end of the audit. Which can be an audit report, a white paper, which is a research document, or an advisory or alert document. Which is for the highest preliminary risk issues identified.

The scope method and exclusions section are for describing in detail the timing of the audit providing an overview of the fil work methods or procedures and for discussing what will not be examined during the fieldwork.
The exclusions often use this section to list out the criteria or policies and procedures and use these procedures to create process flow charts for the major processes that will be examined. Here in this example that would be cash sale inventory and appreciation.
The initial thoughts on the results section summarize where the auditor thinks the highest risks may be prior to fieldwork. This information is based on preliminary data examination or prior audit reports on the subject area. The estimated audit engagement dates allow your internal auditor function to will properly allocate staff to various audit projects.
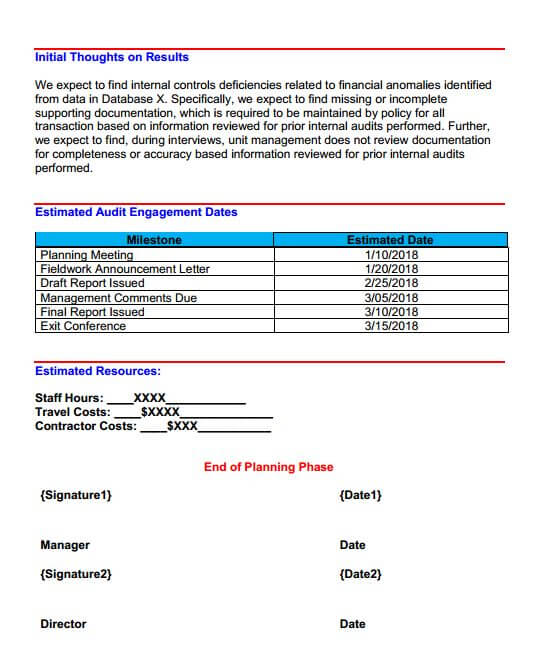
Download the template from here
It also serves as an estimate for when the audit report will be completed. Further, the estimated dates are then used to estimate staff hours travel costs, and contractor costs on the audit project. Once all this information is completed the audit manager director and chief audit executive will approve the audit plan.
Fieldwork
Fieldwork is the process of gathering evidence in analyzing and evaluating that evidence as outlined in the audit work plan and detailed procedures. The audit objectives and procedures should be performed so that the audit report is fully supported by the evidence collected in analyses performed.
Testing controls
When testing controls the auditor reviews activities through reaper performance observation and inspection to see whether the control activities prevent or detect the events as they are supposed to.
For example, during fieldwork, the auditor may use an application to enter an erroneous transaction to see whether the detective control a report that is flagging transaction errors is working properly. For preventative control testing the auditor examine access logs to see whether all persons who had access to the system were properly authorized.
Collecting evidence
Evidence needs to be persuasive and support audit conclusions and recommendations. So remember the types of evidence and how to evaluate evidence for persuasiveness.
Communication
Communication is critical to a successful audit. Each phase of the audit requires discussing important information with both internal and external stakeholders.
Question no #11
Which of the following is a preventive control?
- Walkthroughs of activities
- Segregation of duties
- Transaction reports or
- Error logs
The answers id 2
Walkthroughs transaction reports and error logs are detectives controls they detect an issue but they don’t prevent it segregation of duties allows more than one user to be involved in a process that reduces errors and the risk of fraud.
Fieldwork testing
In this section of we will discuss fieldwork testing. And relate testing to various accounts on the balance sheet and income statement. Since these are the two primary financial statements of concern when performing an internal controls audit over financial reporting.
A balance sheet is a financial statement containing the assets liabilities and equity of a business or organization at a particular point in time. Balance sheets are usually produced monthly, quarterly, which is every three months and annually.
So how does the balance sheet relate to the audit of our internal control for financial reporting? The balance sheet can assist auditors in performing the test of details of balances. If the auditor assesses risk for the sales and collection cycle is very high, he or she may perform tests of details of balances.
For sales and collections, this will likely involve the examination of cash, accounts receivable, and inventory accounts listed on the balance sheet.
To examine the balance sheet accounts, we can either vouch down or go from the cash accounts receivable or inventory balance to the supporting sales invoices cash payment records, and shipping records to see if they all exist and add up to these balances.
Or we could trace up by selecting a sample of the sales invoices shipping records and cash payment records for our audit scope period and examine whether all these transactions were recorded on the balance sheet.
The income statement is a financial statement. That reports a company’s financial performance over a specific accounting period. Financial performance is determined by examining income or revenue and expenses through operating and non-operating activities.
So how does the income statement relate to our internal controls audio over financial reporting? The income statement can assist in performing the test details of balances in addition to the balance sheet.
If the auditor assesses risk for the sales in the collection cycle or sales in the cash receipt cycle is very high the auditor may wish to examine the balances of the sales revenue, sales returns, sales discounts, and cost of goods sold accounts on the income statement.
The auditor can do so by vouching down from these income statement account balances to the supporting documents to see if all transactions that makeup these account balances exist. The auditor can also trace up by selecting a sample of supporting documents such as sales receipts, cash drawer, accounts inventory price lists and sales return receipts to see whether all transactions are reflected in the income statement accounts. For sales revenue, sales returns, sell discounts, and the cost of goods sold.
Reporting
Audit reports for internal controls over financial reporting should include information about management statements on internal controls. It should also include auditors’ descriptions of the standards used to perform the audit and whether the audit was performed entirely in compliance with these standards.
Audit findings should also address the condition or state of the issues identified the criteria which are the policies and procedures the root cause of the issues and the effect or impact of these issues. Recommendations should address the root cause identified by the auditors.
Question no #12
What is the audit criteria?
- Policies and procedures used to assess controls
- Utter opinion
- Management’s actions or
- The current state of the activities examined
The answer is 1
Otto criteria are the policies and procedures auditors use to compare activities in the process during fieldwork examination.




